
Four popular weight-loss strategies
1. Cut calories
Some experts believe that successfully managing your weight comes down to a simple equation: If you eat fewer calories than you burn, you lose weight. Sounds easy, right? Then why is losing weight so hard?
- Weight loss isn’t a linear event over time. When you cut calories, you may drop weight for the first few weeks, for example, and then something changes. You eat the same number of calories but you lose less weight or no weight at all. That’s because when you lose weight you’re losing water and lean tissue as well as fat, your metabolism slows, and your body changes in other ways. So, in order to continue dropping weight each week, you need to continue cutting calories.
- A calorie isn’t always a calorie. Eating 100 calories of high fructose corn syrup, for example, can have a different effect on your body than eating 100 calories of broccoli. The trick for sustained weight loss is to ditch the foods that are packed with calories but don’t make you feel full (like candy) and replace them with foods that fill you up without being loaded with calories (like vegetables).
- Many of us don’t always eat simply to satisfy hunger. We also turn to food for comfort or to relieve stress—which can quickly derail any weight loss plan.
2. Cut carbs
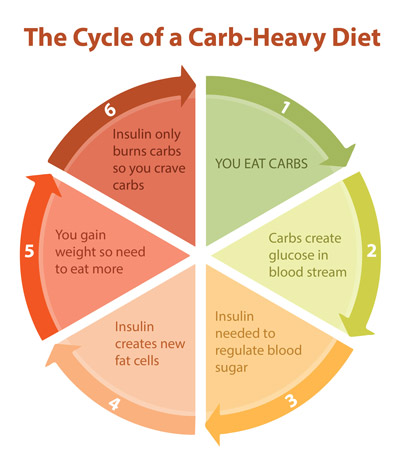
A different way of viewing weight loss identifies the problem as not one of consuming too many calories, but rather the way the body accumulates fat after consuming carbohydrates—in particular the role of the hormone insulin. When you eat a meal, carbohydrates from the food enter your bloodstream as glucose. In order to keep your blood sugar levels in check, your body always burns off this glucose before it burns off fat from a meal.
If you eat a carbohydrate-rich meal (lots of pasta, rice, bread, or French fries, for example), your body releases insulin to help with the influx of all this glucose into your blood. As well as regulating blood sugar levels, insulin does two things: It prevents your fat cells from releasing fat for the body to burn as fuel (because its priority is to burn off the glucose) and it creates more fat cells for storing everything that your body can’t burn off. The result is that you gain weight and your body now requires more fuel to burn, so you eat more. Since insulin only burns carbohydrates, you crave carbs and so begins a vicious cycle of consuming carbs and gaining weight. To lose weight, the reasoning goes, you need to break this cycle by reducing carbs.
Most low-carb diets advocate replacing carbs with protein and fat, which could have some negative long-term effects on your health. If you do try a low-carb diet, you can reduce your risks and limit your intake of saturated and trans fats by choosing lean meats, fish and vegetarian sources of protein, low-fat dairy products, and eating plenty of leafy green and non-starchy vegetables.
3. Cut fat
It’s a mainstay of many diets: if you don’t want to get fat, don’t eat fat. Walk down any grocery store aisle and you’ll be bombarded with reduced-fat snacks, dairy, and packaged meals. But while our low-fat options have exploded, so have obesity rates. So, why haven’t low-fat diets worked for more of us?
- Not all fat is bad. Healthy or “good” fats can actually help to control your weight, as well as manage your moods and fight fatigue. Unsaturated fats found in avocados, nuts, seeds, soy milk, tofu, and fatty fish can help fill you up, while adding a little tasty olive oil to a plate of vegetables, for example, can make it easier to eat healthy food and improve the overall quality of your diet.
- We often make the wrong trade-offs. Many of us make the mistake of swapping fat for the empty calories of sugar and refined carbohydrates. Instead of eating whole-fat yogurt, for example, we eat low- or no-fat versions that are packed with sugar to make up for the loss of taste. Or we swap our fatty breakfast bacon for a muffin or donut that causes rapid spikes in blood sugar.
4. Follow the Mediterranean diet
The Mediterranean diet emphasizes eating good fats and good carbs along with large quantities of fresh fruits and vegetables, nuts, fish, and olive oil—and only modest amounts of meat and cheese. The Mediterranean diet is more than just about food, though. Regular physical activity and sharing meals with others are also major components.
Whatever weight loss strategy you try, it’s important to stay motivated and avoid common dieting pitfalls, such as emotional eating.





